
Kindel Media/Pexels
Pacifying gestures have long been associated with feelings of security and relaxation. Pacifying gestures may also serve as an indicator of deception in adults. This unexpected connection stems from the phenomenon of stress-induced “reversion,” a psychological state in which individuals regress to behaviors associated with earlier stages of development when experiencing heightened stress or anxiety.
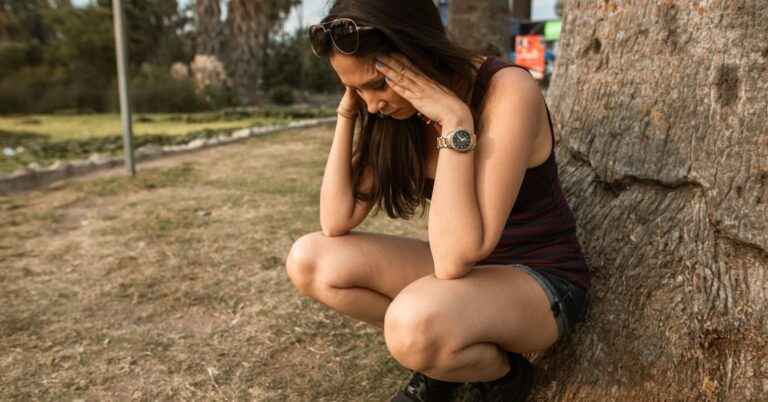
Under normal circumstances, adults exhibit more mature coping mechanisms to deal with stress. However, when faced with overwhelming or unfamiliar situations, they may revert to behaviors that provided comfort and security during childhood. Pacifying gestures in childhood are deeply ingrained and symbolically reassuring acts that can resurface as a means of self-soothing and stress reduction in adulthood.
Deception, by its very nature, is a stress-inducing activity. The cognitive dissonance associated with concealing the truth, the fear of detection, and the potential consequences of being caught can all contribute to heightened levels of anxiety. As a result, individuals engaged in deception may subconsciously seek out pacifiers or other childhood comfort objects to alleviate their stress and regulate their emotions.
Liars will often caress their lips with the tips of their fingers to alleviate the stress of lying. Liars sometimes wipe their hands on the top of their thighs to reduce the tension of lying. Liars sometimes rub their hands together or rub their forearms to reduce the stress of lying. Hand to cheek caresses are also common when people lie. This phenomenon has been observed in various contexts, including job interviews, criminal interrogations, and even political debates. In these situations, individuals may use pacifying gestures as a subtle yet telling sign of their underlying deception.
While this behavior in adults can indicate deception, it is essential to distinguish it from the neutral need for comfort or relaxation. Several factors can help in this identification:
- Context and Timing: The context and timing of pacifier use can provide valuable clues. If an adult suddenly displays pacifying gestures when they have not done so before, particularly when faced with stress or scrutiny, it may signal deception.
- Non-Verbal Cues: Pacifying gestures should be considered alongside other non-verbal cues, such as fidgeting, excessive blinking, or avoiding eye contact. A combination of these behaviors can further strengthen the suspicion of deception.
- Individual Differences: It is crucial to consider individual differences and cultural norms. Some individuals may naturally use pacifiers as a stress reliever, while others may find the act inappropriate or uncommon.
The use of pacifying gestures as an indicator of deception is a relatively new area of research, and more studies are needed to establish its validity and reliability. Additionally, personality traits, cultural backgrounds, and individual experiences can influence pacifier use, making it difficult to generalize research findings.
Despite these limitations, the potential applications of detecting deception through pacifying gestures are intriguing. Law enforcement agencies, for instance, could utilize this knowledge to identify deceptive suspects during interrogations or investigations. Similarly, business negotiators could use pacifier use as a subtle cue to assess the honesty of potential partners or clients. Moreover, understanding the connection between pacifying gestures and deception can enhance self-awareness and improve communication in personal relationships.
Though often associated with childhood, pacifying gestures can provide valuable insights into the complex realm of human behavior.


















+ There are no comments
Add yours